BRITISH MONARCHY…
People who defend the British Monarchy (ARGUMENTS):
- Representing the UK at HOME and ABROAD.
- Settings standards of citizenship and family life.
- Uniting people despite differences.
- Allegiance of the armed forces.
- Maintaining continuity of BRITISH traditions.
- Preserving a CHRISTIAN MORALITY.
MAIN CRITICSMS OF THE MONARCHY (ARGUMENTS):
- This is the potential for political involvement.
- The Monarchy is unrepresentative.
- The Monarchy is overly EXPENSIVE.
- The Monarchy in no longer NECESSARY.
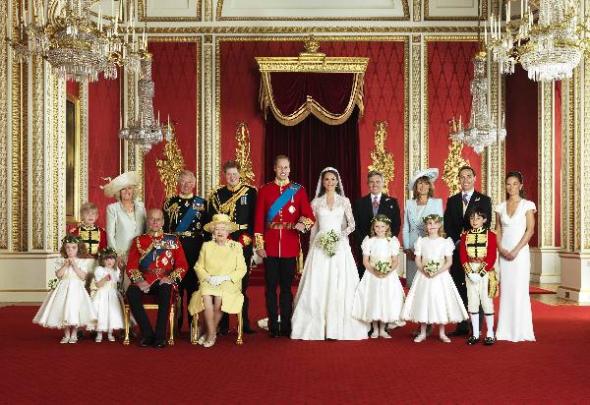
Queen ELIZABETH II became the Monarch on 6 february 1952:
BUCKINGHAM PALACE (Principal Workplace of the BRITISH MONARCH and the official LONDON residence).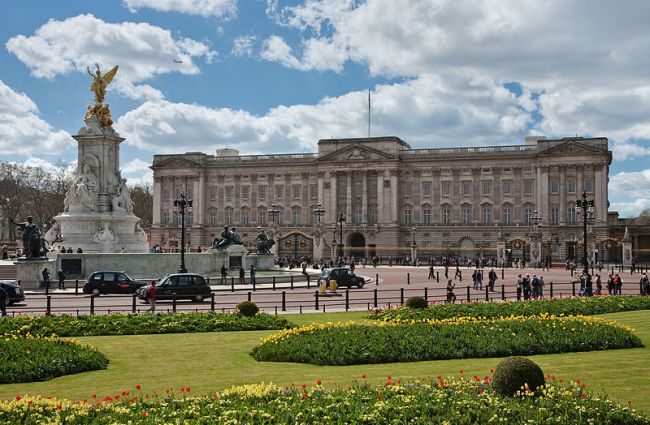
The British Royal Family:
More information:
http://www.historyguy.com/worldbiography/british_royal_family.htm#.UYM6OLWQV2A
BRITISH HISTORY.
British History:
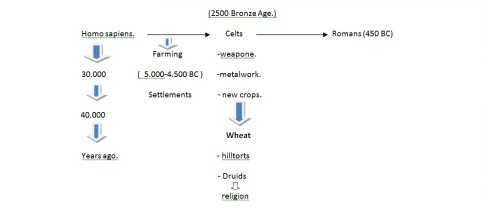
Britain has not always been an island. It became an island after the end of the last ice age, and people who live there lived by FISHING, HUNTING and COLLECTING food, among others.
Neolithic:
Introduction of FARMING (when people learn how to produce food) and that was the result of MIGRATION from the continent.
SETTLEMENTS:
there are CEREMONIALl monuments where people from a particular region gathered together. Some of this monuments were called LENGES and were built according to the position of the SUN. STONEHENGE is one of the most famous.
BRONZE AGE:
2500 BC the BRONZE AGE started, at this time people lived in SETTLEMENTS consisting of ROUND HOUSES grouped together.
THE IRON AGE 800 BC:
About 1250-800 BC the field systems continued in USE.
THE CELTS probably came from CENTRAL EUROPE and were technically advanced, furthermore, they could work with iron and also make better weapons, besides CELTS FARMING TECHNIQUES, in addition they lived in round houses.
CELTS LIFE:
– CELTS were fierce warriors.
– They OFTEN fought naked.
– Their main WEAPONS were: THE SWORD and SPEAR.
MAY: Movies (Comparative presentation of two films from anglophone countries)
MEMBERS:
- Debora Vàsquez
- Sebastian Zamora
- Claude Julio
- Luis Aguilar
- Karen Gonzalez
- Gabriel Barriga
link:
TIME LINE… (Britain’s prehistory)
Questions… ? Hadrian’s Wall.
Watch the segment “Hadrian’s Wall” and answer these questions:
- What was the problem foreseen by Hadrian? He may be unable to maintain his borders
- What problems were the soldiers facing in the Northern part of Britain? They were frozen in winter and there were barbarian incursions.
- What was Hadrian’s conclusion after visiting the front line? Hadrian realize that the soldiers did not works as mush as he wanted.
- Complete the following sentences:
Today Hadrian’s wall has been reduced to it’s a._________foundation_______
It once b._______towered_____15 feet high
…with c._______parapets______rising an additional 6 feet above that
a 9 feet d.____ditch_______was dug at its base
…forcing the potential invaders to e._30____ f._____foot___ climb
- What was the main problem during the construction of the wall, from an engineering point of view? how to get material to the construction site.
- How many men were needed to move heavy rocks to the construction site? 3 legions
- What was the purpose of the mile castles? they were guard post able to house 60 troops
- What buildings were found in each superfort? temple, hospital assembly hall, bath houses
- How long did it take to complete Hadrian’s barrier? 5 years
Roman Roads (summary)
The Roman Army needed better roads to keep the Britons under control, furthermore, the roman generals needed good path to send orders to the roman soldiers, apart from that, the roads were important for moving supplies food and weapons to the soldiers, in peace of time good safe road mean more taxes for the Emperador.
So how did the romans manage to build such straight roads?
The engineers used “the Groma”, that were a pair of boards fastened together onto a cross shape, besides, line with weight were hung in every corner to get a straight line by lining up the weights with a pole, in addition, in forest areas, they built fires in a straight line, because they wanted to use the smoke as a marker for the groma.
UNITS…
I. Historical Background – US – UK.
II. Music.
III. Films.
IV. Television.